
We implemented prefetching algorithms that represent the FS, FA, and AS classes.
Within the FS and FA classes we pick members with small, medium and large
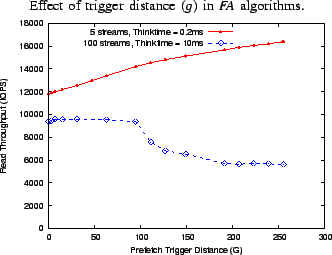
![]() . In Figure 6, we observe that for the FA algorithms there
is no optimal fixed value for
. In Figure 6, we observe that for the FA algorithms there
is no optimal fixed value for ![]() that works for all workloads.
We have chosen
that works for all workloads.
We have chosen ![]() to be half of
to be half of ![]() as that works best for the widest variety of workloads.
For AS algorithms, we chose two popular variants, which adapt
as that works best for the widest variety of workloads.
For AS algorithms, we chose two popular variants, which adapt ![]() linearly (AS
linearly (AS
![]() )
and exponentially (AS
)
and exponentially (AS
![]() ).
We also compare with OBL and the case with no prefetching.
).
We also compare with OBL and the case with no prefetching.
 |