



Next: Time Taken for a
Up: Handling Large States
Previous: Handling Large States
During the state space search, CMC maintains two data structures: a
hash table of states seen during the search, and a queue of states
seen but whose successors are yet to be generated. It is not necessary
to store the entire state in a hash
table [36]. CMC uses a hash compaction
algorithm [36] to store only a small signature
(typically, 8 bytes) for each state in the hash table. By doing so,
the memory requirements of the hash table depend only on the number
of states explored during model checking.
The queue, however, has to maintain the
states in their entirety, as all of the information in the state is
necessary to generate the successor states. However,
the queue has good locality of reference, so much of it can be swapped to
disk during model checking. Moreover, the states in the queue can be
efficiently compressed; as states can simply be regenerated by
remembering the sequence of events that generated them from the
initial system state.
Table 2:
Time taken for a single CMC transition, averaged over the
first million transitions. The experiment involves CMC checking the
TCP model in a server running a 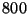 MHz Intel Pentium III
processor with
MHz Intel Pentium III
processor with  KB cache and
KB cache and 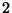 GB of memory.
GB of memory.
| |
Time in microseconds |
| |
State |
Transition |
Hash |
State |
Total |
| |
Restore |
Execution |
Computation |
Store |
|
| Processing Entire States |
656 |
305 |
17816 |
608 |
19385 |
| With Incremental States |
298 |
363 |
2927 |
64 |
3652 |
| With Incremental Heap Canonicalization |
305 |
365 |
1453 |
65 |
2188 |
|
In practice, the large amount of memory available in modern machines
makes managing memory much easier. For instance, a gigabyte hash table
is more than sufficient to explore  million states when using a
million states when using a 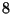 byte compacted signature for each state. The remaining memory can be
allocated for the queue.
As will be shown below, CMC is limited more
by the time required for the state space exploration than by the memory
available.
byte compacted signature for each state. The remaining memory can be
allocated for the queue.
As will be shown below, CMC is limited more
by the time required for the state space exploration than by the memory
available.



Next: Time Taken for a
Up: Handling Large States
Previous: Handling Large States
Madanlal Musuvathi
2004-03-03

![]() million states when using a
million states when using a ![]() byte compacted signature for each state. The remaining memory can be
allocated for the queue.
As will be shown below, CMC is limited more
by the time required for the state space exploration than by the memory
available.
byte compacted signature for each state. The remaining memory can be
allocated for the queue.
As will be shown below, CMC is limited more
by the time required for the state space exploration than by the memory
available.