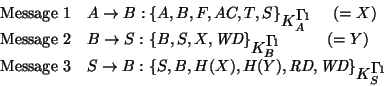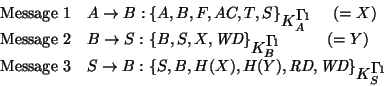Next: Analysis
Up: Protocol description
Previous: Certificate creation
The access-request protocol performs a forward
authentication of access rights from the delegatee to the
server via another user (the delegatee).
In short, to access a file the delegatee signs the delegation
certificate and transmits the result to the file server (FR) by the
exchange of the following messages:
In the protocol description, A and B represent the users Alice and
Bob, S is the FR (server), F is the name of the file in question,
AC are the delegated access rights, and T are two time stamps, one
making the certificate unique the other ensuring that the certificate
expire.
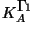 is the private key belonging to A.
Message 1 (or X, in short) is the delegation certificate.
H(X) is the message digest of X, and is essentially B's receipt
from S.
The field RD is data that has been read while WD is
data to be written.
If the access-right is read, WD must be
nil.
The protocol does not distinguish between conventional (networked) or
verbal transfer of the first message -- in both cases the same
information is presented to the server in Message 2.
is the private key belonging to A.
Message 1 (or X, in short) is the delegation certificate.
H(X) is the message digest of X, and is essentially B's receipt
from S.
The field RD is data that has been read while WD is
data to be written.
If the access-right is read, WD must be
nil.
The protocol does not distinguish between conventional (networked) or
verbal transfer of the first message -- in both cases the same
information is presented to the server in Message 2.



Next: Analysis
Up: Protocol description
Previous: Certificate creation
Tage Stabell-Kulo
1999-07-06