
Figure 2 depicts the structure of our algorithm. Fix
the size of RANDOM bottom ![]() to a small constant
fraction of the cache size. The essence of the algorithm is to
compare the absolute values of
to a small constant
fraction of the cache size. The essence of the algorithm is to
compare the absolute values of
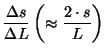 and
and
So far, the time interval for sampling the rates ![]() and
and
![]() has not been fixed. The smaller the time interval the more
adaptive the algorithm, while larger the time interval the
smoother and slower the adaptation. Our algorithm implicitly
selects a time interval based on cache hits. Thus, the rate of
adaptation is derived from and adapts to the workload itself.
Specifically, we
select the time interval to be the time difference between two
successive hits in the bottom of the RANDOM list. In this
case,
has not been fixed. The smaller the time interval the more
adaptive the algorithm, while larger the time interval the
smoother and slower the adaptation. Our algorithm implicitly
selects a time interval based on cache hits. Thus, the rate of
adaptation is derived from and adapts to the workload itself.
Specifically, we
select the time interval to be the time difference between two
successive hits in the bottom of the RANDOM list. In this
case,
![]() is just a constant
is just a constant ![]() , and we measure
, and we measure ![]() during the same interval. Thus, we now need to simply compare
during the same interval. Thus, we now need to simply compare